 [](https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/actions?query=workflow%3Alinux)
[](https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/actions?query=workflow%3Amacos)
[](https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/actions?query=workflow%3Awindows)
[](https://bugs.chromium.org/p/oss-fuzz/issues/list?\%0Acolspec=ID%20Type%20Component%20Status%20Proj%20Reported%20Owner%20\%0ASummary&q=proj%3Dfmt&can=1)
[](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/tagged/fmt)
[](https://securityscorecards.dev/viewer/?uri=github.com/fmtlib/fmt)
**{fmt}** is an open-source formatting library providing a fast and safe
alternative to C stdio and C++ iostreams.
If you like this project, please consider donating to one of the funds
that help victims of the war in Ukraine: .
[Documentation](https://fmt.dev)
[Cheat Sheets](https://hackingcpp.com/cpp/libs/fmt.html)
Q&A: ask questions on [StackOverflow with the tag
fmt](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/tagged/fmt).
Try {fmt} in [Compiler Explorer](https://godbolt.org/z/Eq5763).
# Features
- Simple [format API](https://fmt.dev/latest/api.html) with positional
arguments for localization
- Implementation of [C++20
std::format](https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/utility/format) and
[C++23 std::print](https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/io/print)
- [Format string syntax](https://fmt.dev/latest/syntax.html) similar
to Python\'s
[format](https://docs.python.org/3/library/stdtypes.html#str.format)
- Fast IEEE 754 floating-point formatter with correct rounding,
shortness and round-trip guarantees using the
[Dragonbox](https://github.com/jk-jeon/dragonbox) algorithm
- Portable Unicode support
- Safe [printf
implementation](https://fmt.dev/latest/api.html#printf-formatting)
including the POSIX extension for positional arguments
- Extensibility: [support for user-defined
types](https://fmt.dev/latest/api.html#formatting-user-defined-types)
- High performance: faster than common standard library
implementations of `(s)printf`, iostreams, `to_string` and
`to_chars`, see [Speed tests](#speed-tests) and [Converting a
hundred million integers to strings per
second](http://www.zverovich.net/2020/06/13/fast-int-to-string-revisited.html)
- Small code size both in terms of source code with the minimum
configuration consisting of just three files, `core.h`, `format.h`
and `format-inl.h`, and compiled code; see [Compile time and code
bloat](#compile-time-and-code-bloat)
- Reliability: the library has an extensive set of
[tests](https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/tree/master/test) and is
[continuously fuzzed](https://bugs.chromium.org/p/oss-fuzz/issues/list?colspec=ID%20Type%20Component%20Status%20Proj%20Reported%20Owner%20Summary&q=proj%3Dfmt&can=1)
- Safety: the library is fully type-safe, errors in format strings can
be reported at compile time, automatic memory management prevents
buffer overflow errors
- Ease of use: small self-contained code base, no external
dependencies, permissive MIT
[license](https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/blob/master/LICENSE.rst)
- [Portability](https://fmt.dev/latest/index.html#portability) with
consistent output across platforms and support for older compilers
- Clean warning-free codebase even on high warning levels such as
`-Wall -Wextra -pedantic`
- Locale independence by default
- Optional header-only configuration enabled with the
`FMT_HEADER_ONLY` macro
See the [documentation](https://fmt.dev) for more details.
# Examples
**Print to stdout** ([run](https://godbolt.org/z/Tevcjh))
``` c++
#include
int main() {
fmt::print("Hello, world!\n");
}
```
**Format a string** ([run](https://godbolt.org/z/oK8h33))
``` c++
std::string s = fmt::format("The answer is {}.", 42);
// s == "The answer is 42."
```
**Format a string using positional arguments**
([run](https://godbolt.org/z/Yn7Txe))
``` c++
std::string s = fmt::format("I'd rather be {1} than {0}.", "right", "happy");
// s == "I'd rather be happy than right."
```
**Print chrono durations** ([run](https://godbolt.org/z/K8s4Mc))
``` c++
#include
int main() {
using namespace std::literals::chrono_literals;
fmt::print("Default format: {} {}\n", 42s, 100ms);
fmt::print("strftime-like format: {:%H:%M:%S}\n", 3h + 15min + 30s);
}
```
Output:
Default format: 42s 100ms
strftime-like format: 03:15:30
**Print a container** ([run](https://godbolt.org/z/MxM1YqjE7))
``` c++
#include
#include
int main() {
std::vector v = {1, 2, 3};
fmt::print("{}\n", v);
}
```
Output:
[1, 2, 3]
**Check a format string at compile time**
``` c++
std::string s = fmt::format("{:d}", "I am not a number");
```
This gives a compile-time error in C++20 because `d` is an invalid
format specifier for a string.
**Write a file from a single thread**
``` c++
#include
int main() {
auto out = fmt::output_file("guide.txt");
out.print("Don't {}", "Panic");
}
```
This can be [5 to 9 times faster than
fprintf](http://www.zverovich.net/2020/08/04/optimal-file-buffer-size.html).
**Print with colors and text styles**
``` c++
#include
int main() {
fmt::print(fg(fmt::color::crimson) | fmt::emphasis::bold,
"Hello, {}!\n", "world");
fmt::print(fg(fmt::color::floral_white) | bg(fmt::color::slate_gray) |
fmt::emphasis::underline, "Olá, {}!\n", "Mundo");
fmt::print(fg(fmt::color::steel_blue) | fmt::emphasis::italic,
"你好{}!\n", "世界");
}
```
Output on a modern terminal with Unicode support:

# Benchmarks
## Speed tests
| Library | Method | Run Time, s |
|-------------------|---------------|-------------|
| libc | printf | 0.91 |
| libc++ | std::ostream | 2.49 |
| {fmt} 9.1 | fmt::print | 0.74 |
| Boost Format 1.80 | boost::format | 6.26 |
| Folly Format | folly::format | 1.87 |
{fmt} is the fastest of the benchmarked methods, \~20% faster than
`printf`.
The above results were generated by building `tinyformat_test.cpp` on
macOS 12.6.1 with `clang++ -O3 -DNDEBUG -DSPEED_TEST -DHAVE_FORMAT`, and
taking the best of three runs. In the test, the format string
`"%0.10f:%04d:%+g:%s:%p:%c:%%\n"` or equivalent is filled 2,000,000
times with output sent to `/dev/null`; for further details refer to the
[source](https://github.com/fmtlib/format-benchmark/blob/master/src/tinyformat-test.cc).
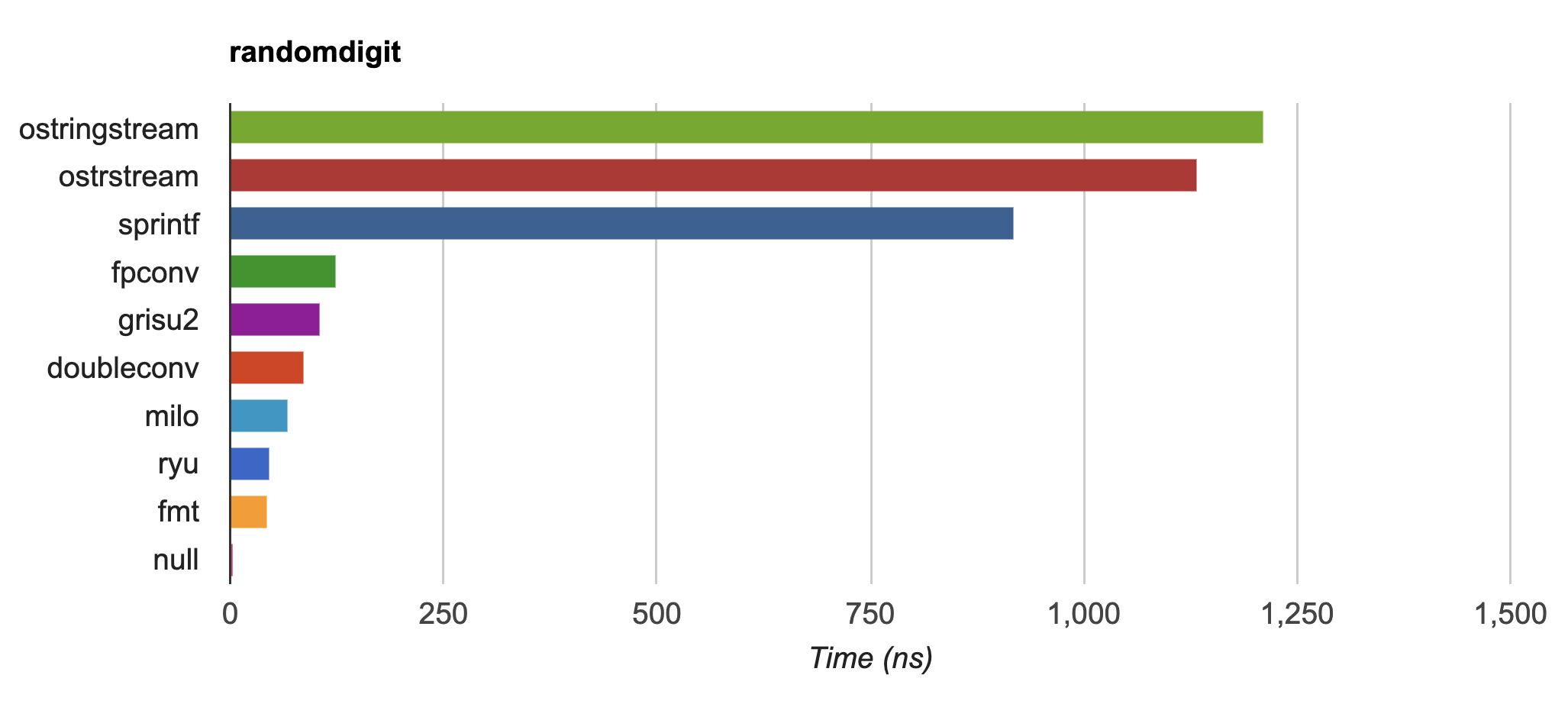
{fmt} is up to 20-30x faster than `std::ostringstream` and `sprintf` on
IEEE754 `float` and `double` formatting
([dtoa-benchmark](https://github.com/fmtlib/dtoa-benchmark)) and faster
than [double-conversion](https://github.com/google/double-conversion)
and [ryu](https://github.com/ulfjack/ryu):
[](https://fmt.dev/unknown_mac64_clang12.0.html)
## Compile time and code bloat
The script
[bloat-test.py](https://github.com/fmtlib/format-benchmark/blob/master/bloat-test.py)
from [format-benchmark](https://github.com/fmtlib/format-benchmark)
tests compile time and code bloat for nontrivial projects. It generates
100 translation units and uses `printf()` or its alternative five times
in each to simulate a medium-sized project. The resulting executable
size and compile time (Apple LLVM version 8.1.0 (clang-802.0.42), macOS
Sierra, best of three) is shown in the following tables.
**Optimized build (-O3)**
| Method | Compile Time, s | Executable size, KiB | Stripped size, KiB |
|---------------|-----------------|----------------------|--------------------|
| printf | 2.6 | 29 | 26 |
| printf+string | 16.4 | 29 | 26 |
| iostreams | 31.1 | 59 | 55 |
| {fmt} | 19.0 | 37 | 34 |
| Boost Format | 91.9 | 226 | 203 |
| Folly Format | 115.7 | 101 | 88 |
As you can see, {fmt} has 60% less overhead in terms of resulting binary
code size compared to iostreams and comes pretty close to `printf`.
Boost Format and Folly Format have the largest overheads.
`printf+string` is the same as `printf` but with an extra ``
include to measure the overhead of the latter.
**Non-optimized build**
| Method | Compile Time, s | Executable size, KiB | Stripped size, KiB |
|---------------|-----------------|----------------------|--------------------|
| printf | 2.2 | 33 | 30 |
| printf+string | 16.0 | 33 | 30 |
| iostreams | 28.3 | 56 | 52 |
| {fmt} | 18.2 | 59 | 50 |
| Boost Format | 54.1 | 365 | 303 |
| Folly Format | 79.9 | 445 | 430 |
`libc`, `lib(std)c++`, and `libfmt` are all linked as shared libraries
to compare formatting function overhead only. Boost Format is a
header-only library so it doesn\'t provide any linkage options.
## Running the tests
Please refer to [Building the
library](https://fmt.dev/latest/usage.html#building-the-library) for
instructions on how to build the library and run the unit tests.
Benchmarks reside in a separate repository,
[format-benchmarks](https://github.com/fmtlib/format-benchmark), so to
run the benchmarks you first need to clone this repository and generate
Makefiles with CMake:
$ git clone --recursive https://github.com/fmtlib/format-benchmark.git
$ cd format-benchmark
$ cmake .
Then you can run the speed test:
$ make speed-test
or the bloat test:
$ make bloat-test
# Migrating code
[clang-tidy](https://clang.llvm.org/extra/clang-tidy/) v17 (not yet
released) provides the
[modernize-use-std-print](https://clang.llvm.org/extra/clang-tidy/checks/modernize/use-std-print.html)
check that is capable of converting occurrences of `printf` and
`fprintf` to `fmt::print` if configured to do so. (By default it
converts to `std::print`.)
# Notable projects using this library
- [0 A.D.](https://play0ad.com/): a free, open-source, cross-platform
real-time strategy game
- [AMPL/MP](https://github.com/ampl/mp): an open-source library for
mathematical programming
- [Apple's FoundationDB](https://github.com/apple/foundationdb): an open-source,
distributed, transactional key-value store
- [Aseprite](https://github.com/aseprite/aseprite): animated sprite
editor & pixel art tool
- [AvioBook](https://www.aviobook.aero/en): a comprehensive aircraft
operations suite
- [Blizzard Battle.net](https://battle.net/): an online gaming
platform
- [Celestia](https://celestia.space/): real-time 3D visualization of
space
- [Ceph](https://ceph.com/): a scalable distributed storage system
- [ccache](https://ccache.dev/): a compiler cache
- [ClickHouse](https://github.com/ClickHouse/ClickHouse): an
analytical database management system
- [Contour](https://github.com/contour-terminal/contour/): a modern
terminal emulator
- [CUAUV](https://cuauv.org/): Cornell University\'s autonomous
underwater vehicle
- [Drake](https://drake.mit.edu/): a planning, control, and analysis
toolbox for nonlinear dynamical systems (MIT)
- [Envoy](https://lyft.github.io/envoy/): C++ L7 proxy and
communication bus (Lyft)
- [FiveM](https://fivem.net/): a modification framework for GTA V
- [fmtlog](https://github.com/MengRao/fmtlog): a performant
fmtlib-style logging library with latency in nanoseconds
- [Folly](https://github.com/facebook/folly): Facebook open-source
library
- [GemRB](https://gemrb.org/): a portable open-source implementation
of Bioware's Infinity Engine
- [Grand Mountain
Adventure](https://store.steampowered.com/app/1247360/Grand_Mountain_Adventure/):
a beautiful open-world ski & snowboarding game
- [HarpyWar/pvpgn](https://github.com/pvpgn/pvpgn-server): Player vs
Player Gaming Network with tweaks
- [KBEngine](https://github.com/kbengine/kbengine): an open-source
MMOG server engine
- [Keypirinha](https://keypirinha.com/): a semantic launcher for
Windows
- [Kodi](https://kodi.tv/) (formerly xbmc): home theater software
- [Knuth](https://kth.cash/): high-performance Bitcoin full-node
- [libunicode](https://github.com/contour-terminal/libunicode/): a
modern C++17 Unicode library
- [MariaDB](https://mariadb.org/): relational database management
system
- [Microsoft Verona](https://github.com/microsoft/verona): research
programming language for concurrent ownership
- [MongoDB](https://mongodb.com/): distributed document database
- [MongoDB Smasher](https://github.com/duckie/mongo_smasher): a small
tool to generate randomized datasets
- [OpenSpace](https://openspaceproject.com/): an open-source
astrovisualization framework
- [PenUltima Online (POL)](https://www.polserver.com/): an MMO server,
compatible with most Ultima Online clients
- [PyTorch](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch): an open-source
machine learning library
- [quasardb](https://www.quasardb.net/): a distributed,
high-performance, associative database
- [Quill](https://github.com/odygrd/quill): asynchronous low-latency
logging library
- [QKW](https://github.com/ravijanjam/qkw): generalizing aliasing to
simplify navigation, and executing complex multi-line terminal
command sequences
- [redis-cerberus](https://github.com/HunanTV/redis-cerberus): a Redis
cluster proxy
- [redpanda](https://vectorized.io/redpanda): a 10x faster Kafka®
replacement for mission-critical systems written in C++
- [rpclib](http://rpclib.net/): a modern C++ msgpack-RPC server and
client library
- [Salesforce Analytics
Cloud](https://www.salesforce.com/analytics-cloud/overview/):
business intelligence software
- [Scylla](https://www.scylladb.com/): a Cassandra-compatible NoSQL
data store that can handle 1 million transactions per second on a
single server
- [Seastar](http://www.seastar-project.org/): an advanced, open-source
C++ framework for high-performance server applications on modern
hardware
- [spdlog](https://github.com/gabime/spdlog): super fast C++ logging
library
- [Stellar](https://www.stellar.org/): financial platform
- [Touch Surgery](https://www.touchsurgery.com/): surgery simulator
- [TrinityCore](https://github.com/TrinityCore/TrinityCore):
open-source MMORPG framework
- [🐙 userver framework](https://userver.tech/): open-source
asynchronous framework with a rich set of abstractions and database
drivers
- [Windows Terminal](https://github.com/microsoft/terminal): the new
Windows terminal
[More\...](https://github.com/search?q=fmtlib&type=Code)
If you are aware of other projects using this library, please let me
know by [email](mailto:victor.zverovich@gmail.com) or by submitting an
[issue](https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues).
# Motivation
So why yet another formatting library?
There are plenty of methods for doing this task, from standard ones like
the printf family of function and iostreams to Boost Format and
FastFormat libraries. The reason for creating a new library is that
every existing solution that I found either had serious issues or
didn\'t provide all the features I needed.
## printf
The good thing about `printf` is that it is pretty fast and readily
available being a part of the C standard library. The main drawback is
that it doesn\'t support user-defined types. `printf` also has safety
issues although they are somewhat mitigated with [\_\_attribute\_\_
((format (printf,
\...))](https://gcc.gnu.org/onlinedocs/gcc/Function-Attributes.html) in
GCC. There is a POSIX extension that adds positional arguments required
for
[i18n](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Internationalization_and_localization)
to `printf` but it is not a part of C99 and may not be available on some
platforms.
## iostreams
The main issue with iostreams is best illustrated with an example:
``` c++
std::cout << std::setprecision(2) << std::fixed << 1.23456 << "\n";
```
which is a lot of typing compared to printf:
``` c++
printf("%.2f\n", 1.23456);
```
Matthew Wilson, the author of FastFormat, called this \"chevron hell\".
iostreams don\'t support positional arguments by design.
The good part is that iostreams support user-defined types and are safe
although error handling is awkward.
## Boost Format
This is a very powerful library that supports both `printf`-like format
strings and positional arguments. Its main drawback is performance.
According to various benchmarks, it is much slower than other methods
considered here. Boost Format also has excessive build times and severe
code bloat issues (see [Benchmarks](#benchmarks)).
## FastFormat
This is an interesting library that is fast, safe, and has positional
arguments. However, it has significant limitations, citing its author:
> Three features that have no hope of being accommodated within the
> current design are:
>
> - Leading zeros (or any other non-space padding)
> - Octal/hexadecimal encoding
> - Runtime width/alignment specification
It is also quite big and has a heavy dependency, STLSoft, which might be
too restrictive for using it in some projects.
## Boost Spirit.Karma
This is not a formatting library but I decided to include it here for
completeness. As iostreams, it suffers from the problem of mixing
verbatim text with arguments. The library is pretty fast, but slower on
integer formatting than `fmt::format_to` with format string compilation
on Karma\'s own benchmark, see [Converting a hundred million integers to
strings per
second](http://www.zverovich.net/2020/06/13/fast-int-to-string-revisited.html).
# License
{fmt} is distributed under the MIT
[license](https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/blob/master/LICENSE).
# Documentation License
The [Format String Syntax](https://fmt.dev/latest/syntax.html) section
in the documentation is based on the one from Python [string module
documentation](https://docs.python.org/3/library/string.html#module-string).
For this reason, the documentation is distributed under the Python
Software Foundation license available in
[doc/python-license.txt](https://raw.github.com/fmtlib/fmt/master/doc/python-license.txt).
It only applies if you distribute the documentation of {fmt}.
# Maintainers
The {fmt} library is maintained by Victor Zverovich
([vitaut](https://github.com/vitaut)) with contributions from many other
people. See
[Contributors](https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/graphs/contributors) and
[Releases](https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/releases) for some of the
names. Let us know if your contribution is not listed or mentioned
incorrectly and we\'ll make it right.
# Security Policy
To report a security issue, please disclose it at [security
advisory](https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/security/advisories/new).
This project is maintained by a team of volunteers on a
reasonable-effort basis. As such, please give us at least 90 days to
work on a fix before public exposure.
[](https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/actions?query=workflow%3Alinux)
[](https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/actions?query=workflow%3Amacos)
[](https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/actions?query=workflow%3Awindows)
[](https://bugs.chromium.org/p/oss-fuzz/issues/list?\%0Acolspec=ID%20Type%20Component%20Status%20Proj%20Reported%20Owner%20\%0ASummary&q=proj%3Dfmt&can=1)
[](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/tagged/fmt)
[](https://securityscorecards.dev/viewer/?uri=github.com/fmtlib/fmt)
**{fmt}** is an open-source formatting library providing a fast and safe
alternative to C stdio and C++ iostreams.
If you like this project, please consider donating to one of the funds
that help victims of the war in Ukraine: .
[Documentation](https://fmt.dev)
[Cheat Sheets](https://hackingcpp.com/cpp/libs/fmt.html)
Q&A: ask questions on [StackOverflow with the tag
fmt](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/tagged/fmt).
Try {fmt} in [Compiler Explorer](https://godbolt.org/z/Eq5763).
# Features
- Simple [format API](https://fmt.dev/latest/api.html) with positional
arguments for localization
- Implementation of [C++20
std::format](https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/utility/format) and
[C++23 std::print](https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/io/print)
- [Format string syntax](https://fmt.dev/latest/syntax.html) similar
to Python\'s
[format](https://docs.python.org/3/library/stdtypes.html#str.format)
- Fast IEEE 754 floating-point formatter with correct rounding,
shortness and round-trip guarantees using the
[Dragonbox](https://github.com/jk-jeon/dragonbox) algorithm
- Portable Unicode support
- Safe [printf
implementation](https://fmt.dev/latest/api.html#printf-formatting)
including the POSIX extension for positional arguments
- Extensibility: [support for user-defined
types](https://fmt.dev/latest/api.html#formatting-user-defined-types)
- High performance: faster than common standard library
implementations of `(s)printf`, iostreams, `to_string` and
`to_chars`, see [Speed tests](#speed-tests) and [Converting a
hundred million integers to strings per
second](http://www.zverovich.net/2020/06/13/fast-int-to-string-revisited.html)
- Small code size both in terms of source code with the minimum
configuration consisting of just three files, `core.h`, `format.h`
and `format-inl.h`, and compiled code; see [Compile time and code
bloat](#compile-time-and-code-bloat)
- Reliability: the library has an extensive set of
[tests](https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/tree/master/test) and is
[continuously fuzzed](https://bugs.chromium.org/p/oss-fuzz/issues/list?colspec=ID%20Type%20Component%20Status%20Proj%20Reported%20Owner%20Summary&q=proj%3Dfmt&can=1)
- Safety: the library is fully type-safe, errors in format strings can
be reported at compile time, automatic memory management prevents
buffer overflow errors
- Ease of use: small self-contained code base, no external
dependencies, permissive MIT
[license](https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/blob/master/LICENSE.rst)
- [Portability](https://fmt.dev/latest/index.html#portability) with
consistent output across platforms and support for older compilers
- Clean warning-free codebase even on high warning levels such as
`-Wall -Wextra -pedantic`
- Locale independence by default
- Optional header-only configuration enabled with the
`FMT_HEADER_ONLY` macro
See the [documentation](https://fmt.dev) for more details.
# Examples
**Print to stdout** ([run](https://godbolt.org/z/Tevcjh))
``` c++
#include
int main() {
fmt::print("Hello, world!\n");
}
```
**Format a string** ([run](https://godbolt.org/z/oK8h33))
``` c++
std::string s = fmt::format("The answer is {}.", 42);
// s == "The answer is 42."
```
**Format a string using positional arguments**
([run](https://godbolt.org/z/Yn7Txe))
``` c++
std::string s = fmt::format("I'd rather be {1} than {0}.", "right", "happy");
// s == "I'd rather be happy than right."
```
**Print chrono durations** ([run](https://godbolt.org/z/K8s4Mc))
``` c++
#include
int main() {
using namespace std::literals::chrono_literals;
fmt::print("Default format: {} {}\n", 42s, 100ms);
fmt::print("strftime-like format: {:%H:%M:%S}\n", 3h + 15min + 30s);
}
```
Output:
Default format: 42s 100ms
strftime-like format: 03:15:30
**Print a container** ([run](https://godbolt.org/z/MxM1YqjE7))
``` c++
#include
#include
int main() {
std::vector v = {1, 2, 3};
fmt::print("{}\n", v);
}
```
Output:
[1, 2, 3]
**Check a format string at compile time**
``` c++
std::string s = fmt::format("{:d}", "I am not a number");
```
This gives a compile-time error in C++20 because `d` is an invalid
format specifier for a string.
**Write a file from a single thread**
``` c++
#include
int main() {
auto out = fmt::output_file("guide.txt");
out.print("Don't {}", "Panic");
}
```
This can be [5 to 9 times faster than
fprintf](http://www.zverovich.net/2020/08/04/optimal-file-buffer-size.html).
**Print with colors and text styles**
``` c++
#include
int main() {
fmt::print(fg(fmt::color::crimson) | fmt::emphasis::bold,
"Hello, {}!\n", "world");
fmt::print(fg(fmt::color::floral_white) | bg(fmt::color::slate_gray) |
fmt::emphasis::underline, "Olá, {}!\n", "Mundo");
fmt::print(fg(fmt::color::steel_blue) | fmt::emphasis::italic,
"你好{}!\n", "世界");
}
```
Output on a modern terminal with Unicode support:

# Benchmarks
## Speed tests
| Library | Method | Run Time, s |
|-------------------|---------------|-------------|
| libc | printf | 0.91 |
| libc++ | std::ostream | 2.49 |
| {fmt} 9.1 | fmt::print | 0.74 |
| Boost Format 1.80 | boost::format | 6.26 |
| Folly Format | folly::format | 1.87 |
{fmt} is the fastest of the benchmarked methods, \~20% faster than
`printf`.
The above results were generated by building `tinyformat_test.cpp` on
macOS 12.6.1 with `clang++ -O3 -DNDEBUG -DSPEED_TEST -DHAVE_FORMAT`, and
taking the best of three runs. In the test, the format string
`"%0.10f:%04d:%+g:%s:%p:%c:%%\n"` or equivalent is filled 2,000,000
times with output sent to `/dev/null`; for further details refer to the
[source](https://github.com/fmtlib/format-benchmark/blob/master/src/tinyformat-test.cc).
{fmt} is up to 20-30x faster than `std::ostringstream` and `sprintf` on
IEEE754 `float` and `double` formatting
([dtoa-benchmark](https://github.com/fmtlib/dtoa-benchmark)) and faster
than [double-conversion](https://github.com/google/double-conversion)
and [ryu](https://github.com/ulfjack/ryu):
[](https://fmt.dev/unknown_mac64_clang12.0.html)
## Compile time and code bloat
The script
[bloat-test.py](https://github.com/fmtlib/format-benchmark/blob/master/bloat-test.py)
from [format-benchmark](https://github.com/fmtlib/format-benchmark)
tests compile time and code bloat for nontrivial projects. It generates
100 translation units and uses `printf()` or its alternative five times
in each to simulate a medium-sized project. The resulting executable
size and compile time (Apple LLVM version 8.1.0 (clang-802.0.42), macOS
Sierra, best of three) is shown in the following tables.
**Optimized build (-O3)**
| Method | Compile Time, s | Executable size, KiB | Stripped size, KiB |
|---------------|-----------------|----------------------|--------------------|
| printf | 2.6 | 29 | 26 |
| printf+string | 16.4 | 29 | 26 |
| iostreams | 31.1 | 59 | 55 |
| {fmt} | 19.0 | 37 | 34 |
| Boost Format | 91.9 | 226 | 203 |
| Folly Format | 115.7 | 101 | 88 |
As you can see, {fmt} has 60% less overhead in terms of resulting binary
code size compared to iostreams and comes pretty close to `printf`.
Boost Format and Folly Format have the largest overheads.
`printf+string` is the same as `printf` but with an extra ``
include to measure the overhead of the latter.
**Non-optimized build**
| Method | Compile Time, s | Executable size, KiB | Stripped size, KiB |
|---------------|-----------------|----------------------|--------------------|
| printf | 2.2 | 33 | 30 |
| printf+string | 16.0 | 33 | 30 |
| iostreams | 28.3 | 56 | 52 |
| {fmt} | 18.2 | 59 | 50 |
| Boost Format | 54.1 | 365 | 303 |
| Folly Format | 79.9 | 445 | 430 |
`libc`, `lib(std)c++`, and `libfmt` are all linked as shared libraries
to compare formatting function overhead only. Boost Format is a
header-only library so it doesn\'t provide any linkage options.
## Running the tests
Please refer to [Building the
library](https://fmt.dev/latest/usage.html#building-the-library) for
instructions on how to build the library and run the unit tests.
Benchmarks reside in a separate repository,
[format-benchmarks](https://github.com/fmtlib/format-benchmark), so to
run the benchmarks you first need to clone this repository and generate
Makefiles with CMake:
$ git clone --recursive https://github.com/fmtlib/format-benchmark.git
$ cd format-benchmark
$ cmake .
Then you can run the speed test:
$ make speed-test
or the bloat test:
$ make bloat-test
# Migrating code
[clang-tidy](https://clang.llvm.org/extra/clang-tidy/) v17 (not yet
released) provides the
[modernize-use-std-print](https://clang.llvm.org/extra/clang-tidy/checks/modernize/use-std-print.html)
check that is capable of converting occurrences of `printf` and
`fprintf` to `fmt::print` if configured to do so. (By default it
converts to `std::print`.)
# Notable projects using this library
- [0 A.D.](https://play0ad.com/): a free, open-source, cross-platform
real-time strategy game
- [AMPL/MP](https://github.com/ampl/mp): an open-source library for
mathematical programming
- [Apple's FoundationDB](https://github.com/apple/foundationdb): an open-source,
distributed, transactional key-value store
- [Aseprite](https://github.com/aseprite/aseprite): animated sprite
editor & pixel art tool
- [AvioBook](https://www.aviobook.aero/en): a comprehensive aircraft
operations suite
- [Blizzard Battle.net](https://battle.net/): an online gaming
platform
- [Celestia](https://celestia.space/): real-time 3D visualization of
space
- [Ceph](https://ceph.com/): a scalable distributed storage system
- [ccache](https://ccache.dev/): a compiler cache
- [ClickHouse](https://github.com/ClickHouse/ClickHouse): an
analytical database management system
- [Contour](https://github.com/contour-terminal/contour/): a modern
terminal emulator
- [CUAUV](https://cuauv.org/): Cornell University\'s autonomous
underwater vehicle
- [Drake](https://drake.mit.edu/): a planning, control, and analysis
toolbox for nonlinear dynamical systems (MIT)
- [Envoy](https://lyft.github.io/envoy/): C++ L7 proxy and
communication bus (Lyft)
- [FiveM](https://fivem.net/): a modification framework for GTA V
- [fmtlog](https://github.com/MengRao/fmtlog): a performant
fmtlib-style logging library with latency in nanoseconds
- [Folly](https://github.com/facebook/folly): Facebook open-source
library
- [GemRB](https://gemrb.org/): a portable open-source implementation
of Bioware's Infinity Engine
- [Grand Mountain
Adventure](https://store.steampowered.com/app/1247360/Grand_Mountain_Adventure/):
a beautiful open-world ski & snowboarding game
- [HarpyWar/pvpgn](https://github.com/pvpgn/pvpgn-server): Player vs
Player Gaming Network with tweaks
- [KBEngine](https://github.com/kbengine/kbengine): an open-source
MMOG server engine
- [Keypirinha](https://keypirinha.com/): a semantic launcher for
Windows
- [Kodi](https://kodi.tv/) (formerly xbmc): home theater software
- [Knuth](https://kth.cash/): high-performance Bitcoin full-node
- [libunicode](https://github.com/contour-terminal/libunicode/): a
modern C++17 Unicode library
- [MariaDB](https://mariadb.org/): relational database management
system
- [Microsoft Verona](https://github.com/microsoft/verona): research
programming language for concurrent ownership
- [MongoDB](https://mongodb.com/): distributed document database
- [MongoDB Smasher](https://github.com/duckie/mongo_smasher): a small
tool to generate randomized datasets
- [OpenSpace](https://openspaceproject.com/): an open-source
astrovisualization framework
- [PenUltima Online (POL)](https://www.polserver.com/): an MMO server,
compatible with most Ultima Online clients
- [PyTorch](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch): an open-source
machine learning library
- [quasardb](https://www.quasardb.net/): a distributed,
high-performance, associative database
- [Quill](https://github.com/odygrd/quill): asynchronous low-latency
logging library
- [QKW](https://github.com/ravijanjam/qkw): generalizing aliasing to
simplify navigation, and executing complex multi-line terminal
command sequences
- [redis-cerberus](https://github.com/HunanTV/redis-cerberus): a Redis
cluster proxy
- [redpanda](https://vectorized.io/redpanda): a 10x faster Kafka®
replacement for mission-critical systems written in C++
- [rpclib](http://rpclib.net/): a modern C++ msgpack-RPC server and
client library
- [Salesforce Analytics
Cloud](https://www.salesforce.com/analytics-cloud/overview/):
business intelligence software
- [Scylla](https://www.scylladb.com/): a Cassandra-compatible NoSQL
data store that can handle 1 million transactions per second on a
single server
- [Seastar](http://www.seastar-project.org/): an advanced, open-source
C++ framework for high-performance server applications on modern
hardware
- [spdlog](https://github.com/gabime/spdlog): super fast C++ logging
library
- [Stellar](https://www.stellar.org/): financial platform
- [Touch Surgery](https://www.touchsurgery.com/): surgery simulator
- [TrinityCore](https://github.com/TrinityCore/TrinityCore):
open-source MMORPG framework
- [🐙 userver framework](https://userver.tech/): open-source
asynchronous framework with a rich set of abstractions and database
drivers
- [Windows Terminal](https://github.com/microsoft/terminal): the new
Windows terminal
[More\...](https://github.com/search?q=fmtlib&type=Code)
If you are aware of other projects using this library, please let me
know by [email](mailto:victor.zverovich@gmail.com) or by submitting an
[issue](https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues).
# Motivation
So why yet another formatting library?
There are plenty of methods for doing this task, from standard ones like
the printf family of function and iostreams to Boost Format and
FastFormat libraries. The reason for creating a new library is that
every existing solution that I found either had serious issues or
didn\'t provide all the features I needed.
## printf
The good thing about `printf` is that it is pretty fast and readily
available being a part of the C standard library. The main drawback is
that it doesn\'t support user-defined types. `printf` also has safety
issues although they are somewhat mitigated with [\_\_attribute\_\_
((format (printf,
\...))](https://gcc.gnu.org/onlinedocs/gcc/Function-Attributes.html) in
GCC. There is a POSIX extension that adds positional arguments required
for
[i18n](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Internationalization_and_localization)
to `printf` but it is not a part of C99 and may not be available on some
platforms.
## iostreams
The main issue with iostreams is best illustrated with an example:
``` c++
std::cout << std::setprecision(2) << std::fixed << 1.23456 << "\n";
```
which is a lot of typing compared to printf:
``` c++
printf("%.2f\n", 1.23456);
```
Matthew Wilson, the author of FastFormat, called this \"chevron hell\".
iostreams don\'t support positional arguments by design.
The good part is that iostreams support user-defined types and are safe
although error handling is awkward.
## Boost Format
This is a very powerful library that supports both `printf`-like format
strings and positional arguments. Its main drawback is performance.
According to various benchmarks, it is much slower than other methods
considered here. Boost Format also has excessive build times and severe
code bloat issues (see [Benchmarks](#benchmarks)).
## FastFormat
This is an interesting library that is fast, safe, and has positional
arguments. However, it has significant limitations, citing its author:
> Three features that have no hope of being accommodated within the
> current design are:
>
> - Leading zeros (or any other non-space padding)
> - Octal/hexadecimal encoding
> - Runtime width/alignment specification
It is also quite big and has a heavy dependency, STLSoft, which might be
too restrictive for using it in some projects.
## Boost Spirit.Karma
This is not a formatting library but I decided to include it here for
completeness. As iostreams, it suffers from the problem of mixing
verbatim text with arguments. The library is pretty fast, but slower on
integer formatting than `fmt::format_to` with format string compilation
on Karma\'s own benchmark, see [Converting a hundred million integers to
strings per
second](http://www.zverovich.net/2020/06/13/fast-int-to-string-revisited.html).
# License
{fmt} is distributed under the MIT
[license](https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/blob/master/LICENSE).
# Documentation License
The [Format String Syntax](https://fmt.dev/latest/syntax.html) section
in the documentation is based on the one from Python [string module
documentation](https://docs.python.org/3/library/string.html#module-string).
For this reason, the documentation is distributed under the Python
Software Foundation license available in
[doc/python-license.txt](https://raw.github.com/fmtlib/fmt/master/doc/python-license.txt).
It only applies if you distribute the documentation of {fmt}.
# Maintainers
The {fmt} library is maintained by Victor Zverovich
([vitaut](https://github.com/vitaut)) with contributions from many other
people. See
[Contributors](https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/graphs/contributors) and
[Releases](https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/releases) for some of the
names. Let us know if your contribution is not listed or mentioned
incorrectly and we\'ll make it right.
# Security Policy
To report a security issue, please disclose it at [security
advisory](https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/security/advisories/new).
This project is maintained by a team of volunteers on a
reasonable-effort basis. As such, please give us at least 90 days to
work on a fix before public exposure.
 [](https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/actions?query=workflow%3Alinux)
[](https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/actions?query=workflow%3Amacos)
[](https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/actions?query=workflow%3Awindows)
[](https://bugs.chromium.org/p/oss-fuzz/issues/list?\%0Acolspec=ID%20Type%20Component%20Status%20Proj%20Reported%20Owner%20\%0ASummary&q=proj%3Dfmt&can=1)
[](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/tagged/fmt)
[](https://securityscorecards.dev/viewer/?uri=github.com/fmtlib/fmt)
**{fmt}** is an open-source formatting library providing a fast and safe
alternative to C stdio and C++ iostreams.
If you like this project, please consider donating to one of the funds
that help victims of the war in Ukraine:
[](https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/actions?query=workflow%3Alinux)
[](https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/actions?query=workflow%3Amacos)
[](https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/actions?query=workflow%3Awindows)
[](https://bugs.chromium.org/p/oss-fuzz/issues/list?\%0Acolspec=ID%20Type%20Component%20Status%20Proj%20Reported%20Owner%20\%0ASummary&q=proj%3Dfmt&can=1)
[](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/tagged/fmt)
[](https://securityscorecards.dev/viewer/?uri=github.com/fmtlib/fmt)
**{fmt}** is an open-source formatting library providing a fast and safe
alternative to C stdio and C++ iostreams.
If you like this project, please consider donating to one of the funds
that help victims of the war in Ukraine: