| .. | ||
| atwilc3000 | ||
| bcm | ||
| cc256x | ||
| csr | ||
| da14581 | ||
| em9301 | ||
| stlc2500d | ||
| tc3566x | ||
| zephyr | ||
| README.md | ||
In this chapter, we first explain how Bluetooth chipsets are connected physically and then provide information about popular Bluetooth chipset and their use with BTstack.
HCI Interface
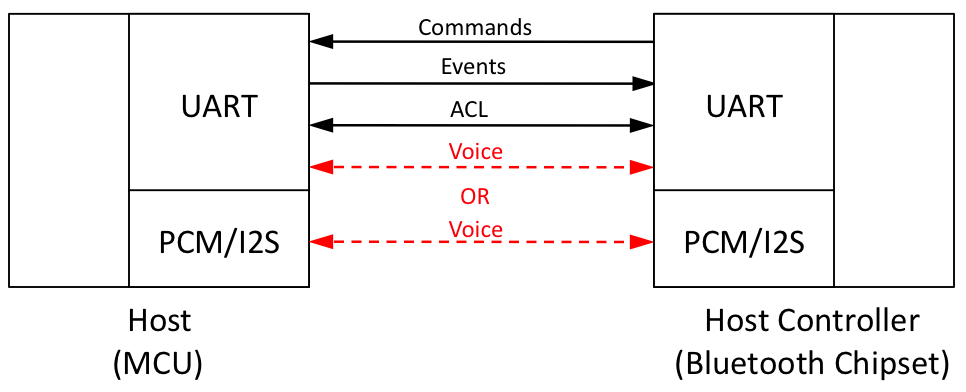
The communication between a Host (a computer or an MCU) and a Host Controller (the actual Bluetooth chipset) follows the Host Controller Interface (HCI), see {@fig:HostChipsetConnection}. HCI defines how commands, events, asynchronous and synchronous data packets are exchanged. Asynchronous packets (ACL) are used for data transfer, while synchronous packets (SCO) are used for Voice with the Headset and the Hands-Free Profiles.
HCI H2
On desktop-class computers incl. laptops, USB is mainly used as HCI transport layer. For USB Bluetooth chipsets, there is little variation: most USB dongles on the market currently contain a Broadcom BCM20702 or a CSR 851x chipset. It is also called H2.
On embedded systems, UART connections are used instead, although USB could be used as well.
For UART connections, different transport layer variants exist.
HCI H4
The most common one is the official "UART Transport", also called H4. It requires hardware flow control via the CTS/RTS lines and assumes no errors on the UART lines.
HCI H5
The "Three-Wire UART Transport", also called H5, makes use of the SLIP protocol to transmit a packet and can deal with packet loss and bit-errors by retransmission. While it is possible to use H5 really with "three wires" without hardware handshake, we recommend to use a full UART with hardware handshake. If your design lacks the hardware handshake, H5 is your only option.
BCSP
The predecessor of H5. The main difference to H5 is that Even Parity is used for BCSP. To use BCSP with BTstack, you use the H5 transport and can call hci_transport_h5_enable_bcsp_mode
eHCILL
Finally, Texas Instruments extended H4 to create the "eHCILL transport" layer that allows both sides to enter sleep mode without loosing synchronisation. While it is easier to implement than H5, it it is only supported by TI chipsets and cannot handle packet loss or bit-errors.
H4 over SPI
Chipsets from Dialog Semiconductor and EM Marin allow to send H4 formatted HCI packets via SPI. SPI has the benefit of a simpler implementation for both Host Controller and Host as it does not require an exact clock. The SPI Master, here the Host, provides the SPI Clock and the SPI Slave (Host Controller) only has to read and update it's data lines when the clock line changes. The EM9304 supports an SPI clock of up to 8 Mhz. However, an additional protocol is needed to let the Host know when the Host Controller has HCI packet for it. Often, an additional GPIO is used to signal this.
HCI Shortcomings
Unfortunately, the HCI standard misses a few relevant details:
-
For UART based connections, the initial baud rate isn't defined but most Bluetooth chipsets use 115200 baud. For better throughput, a higher baud rate is necessary, but there's no standard HCI command to change it. Instead, each vendor had to come up with their own set of vendor-specific commands. Sometimes, additional steps, e.g. doing a warm reset, are necessary to activate the baud rate change as well.
-
Some Bluetooth chipsets don't have a unique MAC address. On start, the MAC address needs to be set, but there's no standard HCI command to set it.
-
SCO data for Voice can either be transmitted via the HCI interface or via an explicit PCM/I2S interface on the chipset. Most chipsets default to the PCM/I2S interface. To use it via USB or for Wide-Band Speech in the Hands-Free Profile, the data needs to be delivered to the host MCU. Newer Bluetooth standards define a HCI command to configure the SCO routing, but it is not implemented in the chipsets we've tested so far. Instead, this is configured in a vendor-specific way as well.
-
In addition, most vendors allow to patch or configure their chipsets at run time by sending custom commands to the chipset. Obviously, this is also vendor dependent.
Documentation and Support
The level of developer documentation and support varies widely between the various Bluetooth chipset providers.
From our experience, only Texas Instruments and EM Microelectronics provide all relevant information directly on their website. Nordic Semiconductor does not officially have Bluetooth chipsets with HCI interface, but their the documentation on their nRF5 series is complete and very informative. TI and Nordic also provide excellent support via their respective web forum.
Broadcom, whose Bluetooth + Wifi division has been acquired by the Cypress Semiconductor Corporation, provides developer documentation only to large customers as far as we know. It's possible to join their Community forum and download the WICED SDK. The WICED SDK is targeted at Wifi + Bluetooth Combo chipsets and contains the necessary chipset patch files.
CSR, which has been acquired by Qualcomm, provides all relevant information on their Support website after signing an NDA.
Chipset Overview
| Chipset | Type | HCI Transport | BD_ADDR (1) | SCO over HCI (2) | LE DLE | Multiple LE Roles | BTstack folder | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atmel ATWILC3000 | LE (4) | H4 | Yes | Don't know | No | No | atwilc3000 | Firmware size: 270 kB |
| Broadcom UART | Dual mode | H4, H5 | Rarely | Probably (2) | No | Maybe (3) | bcm | Max UART baudrate 2 mbps |
| Broadcom USB Dongles | Dual mode | USB | Yes | Yes | No | No | bcm | |
| CSR UART | Dual mode | H4, H5, BCSP | Rarely | No (didn't work) | No | No | csr | |
| CSR USB Dongles | Dual mode | USB | Mostly | Yes | No | No | csr | |
| Dialog DA14581 | LE | H4, SPI | No | n.a. | No | No | da14581 | Official HCI firmware included in BTstack |
| Espressif ESP32 | Dual mode | VHCI | Yes | Probably | Yes | Yes | SoC with Bluetooth and Wifi | |
| EM 9301 | LE | SPI, H4 | No | n.a. | No | No | em9301 | Custom HCI SPI implementation |
| EM 9304 | LE | SPI, H4 | Yes | n.a. | Yes | Yes | em9301 | Custom HCI SPI implementation |
| Nordic nRF | LE | H4 | Fixed Random | n.a. | Yes | Yes | Requires HCI firmware | |
| STM STLC2500D | Classic | H4 | No | No (didn't try) | n.a | n.a. | stlc2500d | Custom deep sleep management not supported |
| Toshiba TC35661 | Dual mode | H4 | No | No (didn't try) | No | No | tc3566 | HCI version not tested. See below |
| TI CC256x, WL183x | Dual mode | H4, H5, eHCILL | Yes | Yes | No | Yes for CC256XC | cc256x | Also WL185x, WL187x, and WL189x |
Notes:
- BD_ADDR: Indciates if Bluetooth chipset compes with its own valid MAC Addess. Better Broadcom and CSR dongles usually come with a MAC address from the dongle manufacturer, but cheaper ones might come with identical addresses.
- SCO over HCI: All Bluetooth Classic chipsets support SCO over HCI, for those that are marked with No, we either didn't try or didn't found enough information to configure it correctly.
- Multiple LE Roles: Apple uses Broadcom Bluetooth+Wifi in their iOS devices and newer iOS versions support multiple concurrent LE roles, so at least some Broadcom models support multiple concurrent LE roles.
- Only BLE qualified - [https://www.bluetooth.org/tpg/QLI_viewQDL.cfm?qid=36402](QDID 99659).
Atmel/Microchip
The ATILC3000 Bluetooth/Wifi combo controller has been used with Linux on embedded devices by Atmel/Microchip. Drivers and documentation are available from a GitHub repository. The ATWILC3000 has a basic HCI implementation stored in ROM and requires a firmware image to be uploaded before it can be used. Only the BLE Controller is currently qualified as [https://www.bluetooth.org/tpg/QLI_viewQDL.cfm?qid=36402](QDID 99659). Please note: the Bluetooth firmware is 270 kB.
BD Addr can be set with vendor-specific command although all chipsets have an official address stored. The BD_ADDR lookup results in "Newport Media Inc." which was acquired by Atmel in 2014.
Baud rate can be set with a custom command.
BTstack integration: btstack_chipset_atwilc3000.c contains the code to download the Bluetooth firmware image into the RAM of the ATWILC3000. After that, it can be normally used by BTstack.
Broadcom/Cypress Semiconductor
Before the Broadcom Wifi+Bluetooth division was taken over by Cypress Semiconductor, it was not possible to buy Broadcom chipset in low quantities. Nevertheless, module manufacturers like Ampak created modules that contained Broadcom BCM chipsets (Bluetooth as well as Bluetooth+Wifi combos) that might already have been pre-tested for FCC and similar certifications. A popular example is the Ampak AP6212A module that contains an BCM 43438A1 and is used on the Raspberry Pi 3, the RedBear Duo, and the RedBear IoT pHAT for older Raspberry Pi models.
The best source for documentation on vendor specific commands so far has been the source code for blueZ and the Bluedroid Bluetooth stack from Android.
Broadcom USB dongles do not require special configuration, however SCO data is not routed over USB by default.
Init scripts: For UART connected chipsets, an init script has to be uploaded after power on. For Bluetooth chipsets that are used in Broadcom Wifi+Bluetooth combos, this file often can be found as a binary file in Linux distributions with the ending '.hcd' or as part of the WICED SDK as C source file that contains the init script as a data array for use without a file system.
To find the correct file, Broadcom chipsets return their model number when asked for their local name.
BTstack supports uploading of the init script in two variants: using .hcd files looked up by name in the posix-h4 port and by linking against the init script in the WICED port. While the init script is processed, the chipsets RTS line goes high, but only 2 ms after the command complete event for the last command from the init script was sent. BTstack waits for 10 ms after receiving the command complete event for the last command to avoid sending before RTS goes high and the command fails.
BD Addr can be set with a custom command. A fixed address is provided on some modules, e.g. the AP6212A, but not on others.
SCO data can be configured with a custom command found in the bluez sources. It works with USB chipsets. The chipsets don't implement the SCO Flow Control that is used by BTstack for UART connected devices. A forum suggests to send SCO packets as fast as they are received since both directions have the same constant speed.
Baud rate can be set with custom command. The baud rate resets during the warm start after uploading the init script. So, the overall scheme is this: start at default baud rate, get local version info, send custom Broadcom baud rate change command, wait for response, set local UART to high baud rate, and then send init script. After sending the last command from the init script, reset the local UART. Finally, send custom baud rate change command, wait for response, and set local UART to high baud rate.
BTstack integration: The common code for all Broadcom chipsets is provided by btstack_chipset_bcm.c. During the setup, btstack_chipset_bcm_instance function is used to get a btstack_chipset_t instance and passed to hci_init function.
SCO Data can be routed over HCI for both USB dongles and UART connections, however BTstack does not provide any form of flow control for UART connections. HSP and HFP Narrow Band Speech is supported via I2C/PCM pins.
CSR / Qualcomm Incorporated
CSR plc has been acquired by Qualcomm Incorporated in August 2015.
Similar to Broadcom, the best source for documentation is the source code for blueZ.
CSR USB dongles do not require special configuration and SCO data is routed over USB by default.
CSR chipset do not require an actual init script in general, but they allow to configure the chipset via so-called PSKEYs. After setting one or more PSKEYs, a warm reset activates the new setting.
BD Addr can be set via PSKEY. A fixed address can be provided if the chipset has some kind of persistent memory to store it. Most USB Bluetooth dongles have a fixed BD ADDR.
SCO data can be configured via a set of PSKEYs. We haven't been able to route SCO data over HCI for UART connections yet.
Baud rate can be set as part of the initial configuration and gets actived by the warm reset.
BTstack integration: The common code for all Broadcom chipsets is provided by btstack_chipset_csr.c. During the setup, btstack_chipset_csr_instance function is used to get a btstack_chipset_t instance and passed to hci_init function. The baud rate is set during the general configuration.
SCO Data is routed over HCI for USB dongles, but not for UART connections. HSP and HFP Narrow Band Speech is supported via I2C/PCM pins.
Dialog Semiconductor
Dialog Semiconductor offers the DA14581, an LE-only SoC that can be programmed with an HCI firmware. The HCI firmware can be uploaded on boot into SRAM or stored in the OTP (One-time programmable) memory, or in an external SPI.
It does not implement the Data Length Extension or supports multiple concurrent roles.
BD Addr fixed to 80:EA:CA:00:00:01. No command in HCI firmware to set it differently. Random addresses could be used instead.
Baud rate: The baud rate is fixed at 115200 with the provided firmware. A higher baud rate could be achieved by re-compiling the HCI firmware using Dialog's HCI SDK.
BTstack integration: btstack_chipset_da14581.c contains the code to download the provided HCI firmware into the SRAM of the DA14581. After that, it can be used as any other HCI chipset.
Espressif ESP32
The ESP32 is a SoC with a built-in Dual mode Bluetooth and Wifi radio. The HCI Controller is implemented in software and accessed via a so called Virtual HCI (VHCI) interface. It supports both LE Data Length Extensions (DLE) as well as multiple LE roles. Flow control between the VHCI and BTstack is problematic as there's no way to stop the VHCI from delivering packets. BTstack impelemts the Host Controller to Host Flow Control to deal with this. Right now, this works for HCI Events and Classic ACL packets but not for LE ACL packets. Espressif is working on a solution for this: https://github.com/espressif/esp-idf/issues/644
EM Microelectronic Marin
For a long time, the EM9301 has been the only Bluetooth Single-Mode LE chipset with an HCI interface. The EM9301 can be connected via SPI or UART. The UART interface does not support hardware flow control and is not recommended for use with BTstack. The SPI mode uses a proprietary but documented extension to implement flow control and signal if the EM9301 has data to send.
In December 2016, EM released the new EM9304 that also features an HCI mode and adds support for optional Bluetooth 4.2. features. It supports the Data Length Extension and up to 8 LE roles. The EM9304 is a larger MCU that allows to run custom code on it. For this, an advanced mechanism to upload configuration and firmware to RAM or into an One-Time-Programmable area of 128 kB is supported. It supports a superset of the vendor specific commands of the EM9301.
EM9304 is used by the 'stm32-l053r8-em9304' port in BTstack. The port.c file also contains an IRQ+DMA-driven implementation of the SPI H4 protocol specified in the datasheet.
BD Addr must be set during startup for EM9301 since it does not have a stored fix address. The EM9304 comes with an valid address stored in Flash/OTP.
SCO data is not supported since it is LE only.
Baud rate could be set for UART mode. For SPI, the master controls the speed via the SPI Clock line. With 3.3V, 16 Mhz is supported.
Init scripts are not required although it is possible to upload small firmware patches to RAM or the OTP memory.
BTstack integration: The common code for the EM9304 is provided by btstack_chipset_em9301.c. During the setup, btstack_chipset_em9301_instance function is used to get a btstack_chipset_t instance and passed to hci_init function. It enables to set the BD Addr during start.
Nordic nRF5 series
The Single-Mode LE chipsets from the Nordic nRF5 series chipsets usually do not have an HCI interface. Instead, they provide an LE Bluetooth Stack as a binary library, the so-called SoftDevices. Developer can write their Bluetooth application on top of this library. Since the chipset can be programmed, it can also be loaded with a firmware that provides a regular HCI H4 interface for a Host.
An interesting feature of the nRF5 chipsets is that they can support multiple LE roles at the same time, e.g. being Central in one connection and a Peripheral in another connection. Also, the nRF52 SoftDevice implementation supports the Bluetooth 4.2 Data Length Extension.
Both nRF5 series, the nRF51 and the nRF52, can be used with an HCI firmware. The nRF51 does not support encrypted connections at the moment (November 18th, 2016) although this might become supported as well.
BD ADDR is not set automatically. However, during production, a 64-bit random number is stored in the each chip. Nordic uses this random number as a random static address in their SoftDevice implementation.
SCO data is not supported since it is LE only.
Baud rate is fixed to 115200 by the patch although the firmware could be extended to support a baud rate change.
Init script is not required.
BTstack integration: Support for a nRF5 chipset with the Zephyr Controller is provided by btstack_chipset_zephyr.c. It queries the static random address during init.
To use these chipsets with BTstack, you need to install an arm-none-eabi gcc toolchain and the nRF5x Command Line Tools incl. the J-Link drivers, checkout the Zephyr project, apply a minimal patch to help with using a random static address, and flash it onto the chipset:
-
Get nrfjprog as part of the nRFx-Command-Line-Tools. Click on Downloads tab on the top and look for your OS.
-
Checkout Zephyr and install toolchain. We recommend using the arm-non-eabi gcc binaries instead of compiling it yourself. At least on OS X, this failed for us.
-
In samples/bluetooth/hci_uart compile the firmware for nRF52 Dev Kit
$ make BOARD=nrf52_pca10040
-
Upload the firmware
$ ./flash_nrf52_pca10040.sh
-
For the nRF51 Dev Kit, use
make BOARD=nrf51_pca10028and./flash_nrf51_10028.shwith the nRF51 kit. -
The nRF5 dev kit acts as an LE HCI Controller with H4 interface.
STMicroelectronics
STMicroelectronics offers the Bluetooth V2.1 + EDR chipset STLC2500D that supports SPI and UART H4 connection.
BD Addr can be set with custom command although all chipsets have an official address stored.
SCO data might work. We didn't try.
Baud rate can be set with custom command. The baud rate change of the chipset happens within 0.5 seconds. At least on BTstack, knowning exactly when the command was fully sent over the UART is non-trivial, so BTstack switches to the new baud rate after 100 ms to expect the command response on the new speed.
Init scripts are not required although it is possible to upload firmware patches.
BTstack integration: Support for the STLC2500C is provided by btstack_chipset_stlc.c. During the setup, btstack_chipset_stlc2500d_instance function is used to get a btstack_chipset_t instance and passed to hci_init function. It enables higher UART baud rate and to set the BD Addr during startup.
Texas Instruments CC256x series
The Texas Instruments CC256x series is currently in its fourth iteration and provides a Classic-only (CC2560), a Dual-mode (CC2564), and a Classic + ANT (CC2567) model. A variant of the Dual-mode chipset is also integrated into TI's WiLink 8 Wifi+Bluetooth combo modules of the WL183x, WL185x, WL187x, and WL189x series. Some of the latter support ANT as well.
The CC256x chipset is connected via an UART connection and supports the H4, H5 (since third iteration), and eHCILL.
The latest generation CC256xC chipsets support multiple LE roles in parallel.
The different CC256x chipset can be identified by the LMP Subversion returned by the hci_read_local_version_information command. TI also uses a numeric way (AKA) to identify their chipsets. The table shows the LMP Subversion and AKA number for the CC256x and the WL18xx series.
| Chipset | LMP Subversion | AKA |
|---|---|---|
| CC2560 | 0x191f | 6.2.31 |
| CC2560A, CC2564, CC2567 | 0x1B0F | 6.6.15 |
| CC256xB | 0x1B90 | 6.7.16 |
| CC256xC | 0x9a1a | 6.12.26 |
| WL18xx | 0xac20 | 11.8.32 |
SCO data is routed to the I2S/PCM interface but can be configured with the HCI_VS_Write_SCO_Configuration command.
Baud rate can be set with HCI_VS_Update_UART_HCI_Baudrate. The chipset confirms the change with a command complete event after which the local UART is set to the new speed. Oddly enough, the CC256x chipsets ignore the incoming CTS line during this particular command complete response.
If you've implemented the hal_uart_dma.h without an additional ring buffer (as recommended!) and you have a bit of delay, e.g. because of thread switching on a RTOS, this could cause a UART overrun. If this happens, BTstack provides a workaround in the HCI H4 transport implementation by adding #define ENABLE_CC256X_BAUDRATE_CHANGE_FLOWCONTROL_BUG_WORKAROUND to your btstack_config.h. If this is enabled, the H4 transport layer will resort to "deep packet inspection" to first check if its a TI controller and then wait for the HCI_VS_Update_UART_HCI_Baudrate. When detected, it will tweak the next UART read to expect the HCI Command Complete event.
BD Addr can be set with [HCI_VS_Write_BD_Addr](2.2.1 HCI_VS_Write_BD_Addr (0xFC06)) although all chipsets have an official address stored.
Init Scripts. In order to use the CC256x chipset an initialization script must be obtained and converted into a C file for use with BTstack. For newer revisions, TI provides a main.bts and a ble_add_on.bts that need to be combined.
The Makefile at chipset/cc256x/Makefile.inc is able to automatically download and convert the requested file. It does this by:
- Downloading one or more BTS files for your chipset.
- Running the Python script:
./convert_bts_init_scripts.py main.bts [ble_add_on.bts] output_file.c
BTstack integration: The common code for all CC256x chipsets is provided by btstack_chipset_cc256x.c. During the setup, btstack_chipset_cc256x_instance function is used to get a btstack_chipset_t instance and passed to hci_init function. btstack_chipset_cc256x_lmp_subversion provides the LMP Subversion for the selected init script.
SCO Data can be routed over HCI, so HFP Wide-Band Speech is supported.
Toshiba
The Toshiba TC35661 Dual-Mode chipset is available in three variants: standalone incl. binary Bluetooth stack, as a module with embedded stack or with a regular HCI interface. The HCI variant has the model number TC35661–007.
We've tried their USB Evaluation Stick that contains an USB-to-UART adapter and the PAN1026 module that contains the TC35661 -501. We have been told by our distributor that the -501 variant also supports the HCI interface. However, while our tests have shown that Classic Bluetooth with SPP works fine with this variant, none of the LE commands work.
SCO data might work. We didn't try.
Baud rate can be set with custom command.
**BD Addr ** must be set with custom command. It does not have a stored valid public BD Addr.
Init Script is not required. A patch file might be uploaded.
BTstack integration: Support for the TC35661 series is provided by btstack_chipset_tc3566x.c. During the setup, btstack_chipset_tc3566x_instance function is used to get a btstack_chipset_t instance and passed to hci_init function. It enables higher UART baud rate and sets the BD Addr during startup.